Eradicating Bed Bugs: Effective Methods

Bed bugs are one of the most challenging pests to control, but with a proper and proactive approach, it can be done. These hardy insects have remarkable resilience when it comes to surviving in human dwellings, so controlling them requires both knowledge and dedication.
Understanding bed bug biology and behavior will help us prepare more effectively for treatment while vigilantly monitoring post-treatment activities reduces the risk of reinfestation. This article provides all you need to know about treating bed bugs in your home, giving advice on preparation techniques along with various treatment approaches available today.
Understanding Bed Bugs
Physical characteristics and life cycle of bed bugs
Bed bugs are small, flat insects with dark yellow-brown or reddish bodies. Adults grow up to 4–5mm long and 1.5 mm wide and usually feed on human blood at night when people are asleep.
Their oval/elongated shape allows them to easily hide in tiny cracks and crevices including seams of mattresses, between bed frame slats, furniture joints or even behind wall outlets and picture frames.
The life cycle of the common bed bug consists of 5 stages: Egg (usually lays 200 during her lifetime), nymphs which molts five times until reaching maturity as an adult male or female after 7 – 10 days depending on temperature.
Common signs and symptoms of bed bug infestation
Bed bug infestations are notoriously difficult to identify due to the insects’ small size and nocturnal lifestyle. Since adult bed bugs rarely leave their hiding places during daylight, signs of an active problem may not be noticeable for a long time.
To determine if there is an infestation present, look out for some common indicators such as:
- Rusty or reddish stains from crushed dead bedbugs on mattresses and linen
- Fecal spots (small dark colored specks produced by the feeding habits of immature forms
- Eggshells from newly hatched nymphs scattered in crevices and furniture joints
- Musty odor caused by pheromones secreted through scent glands located in eggs, larvae, pupae
Identifying the areas most likely to be affected by bed bugs
Identifying the locations where bed bugs may hide is essential for proper treatment. Bed bug infestations typically occur in bedrooms, mattresses and box springs, couches and easy chairs, and headboards or footboards of beds frames are commonly affected.
Other items including baseboards carpet edges behind picture frames curtains crevices near utility outlets or plumbing as well as under loose wallpaper can be harborage areas for these pests. When inspecting for presence of bedbugs it’s important to use a flashlight; these insects are very small so require good lighting- most people would not notice them with just their naked eye alone
Preparation for Bed Bug Treatment
1. Inspection and assessment of the infested areas
Before beginning a bed bug treatment, it is important to carry out an inspection and assessment of the infested areas. This process involves thoroughly inspecting furniture and prop elements for signs such as live bugs or eggs, shed skins, dark spots on mattresses/bedding (blood stains), dried corpses in corners etc.
The inspector should also pay attention to any possible hiding places like:
- Cracks between walls & skirting boards
- Behind picture frames
- Under carpets
- Holes created by woodborers
All potential sources that may harbor infiltrating insects not easy to spot with just bare eyes! After carrying out the inspections professionals can determine which assets need treating prior-to covering up proper control techniques outlined above
2. Decluttering and organizing the affected spaces
Decluttering and organizing affected spaces are important steps for bed bug treatment. Disorganized areas make inspection difficult, causing the infestation to go undetected – which may lead to a worsening situation.
Unnecessary items should be removed and stored away in airtight or plastic bags until they can be treated separately. Other objects like mattresses and drawers should also be organized so that all sides of them are accessible during an extensive visual check up of being free from bed bugs or eggs.
3. Safe handling and containment of infested items
When preparing for a successful bed bug treatment, it is important to take the necessary steps to ensure safe handling and containment of infested items. This will greatly reduce the spread of these pests throughout your home or business premises. First, all affected clothes should be immediately bagged into vacuum-sealed containers.
All upholstered furniture must also be contained in sealed bags separately from other fabrics and clothing that are not contaminated with bed bugs. Carefully inspect any secondhand objects you plan on bringing in before doing so as they could harbor an active infestation without showing signs themselves at first glance!
4. Taking necessary precautions to prevent further infestation
In preparation for bed bug treatment, it is important to take precautions in order to prevent further infestation. This includes refraining from moving items that may be suspected of having a bed bug presence and properly discarding potentially contaminated materials through sealed bags or disposals such as vacuums with rigid hoses.
It also involves cleaning frequently used areas thoroughly, avoiding overcrowding furniture and personal belongings, checking secondhand goods before bringing them into the home environment, sealing off any existing cracks and crevices on surfaces around beds where eggs can easily hide among fabric folds, and washing all linens (such as sheets) at high temperatures regularly using hot water cycles when possible.
Non-Chemical Bed Bug Treatment Methods
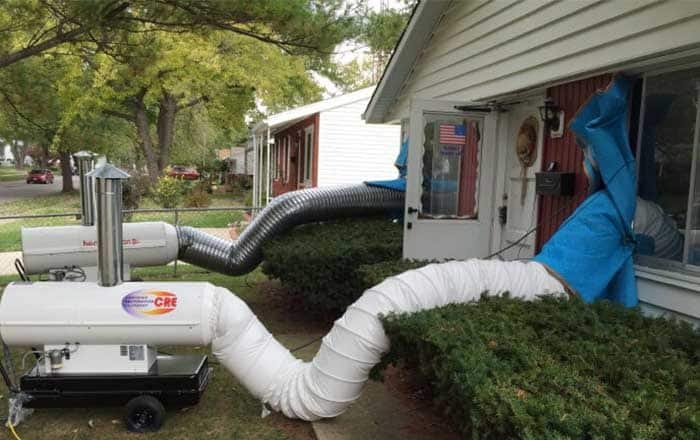
1. Heat treatment: Explanation of heat treatment process and its effectiveness
Heat treatment is a non-chemical bed bug eradication method used to effectively eliminate all stages of the life cycle. Temperatures over 120 degrees Fahrenheit are needed for at least ninety minutes in order to achieve success with this type of treatment, and special equipment such as heaters, fans and monitoring devices must be utilized throughout the process.
Heat treatments have been proven safe even around electronics and delicate items, making them an efficient option for many hard-to-reach areas that pesticides sometimes cannot reach.
2. Vacuuming and steaming: Proper techniques for vacuuming and steaming infested areas
Vacuuming and steaming are effective non-chemical methods for treating bed bug infestations. For vacuuming, be sure to use a comprehensive suction with attachments to reach tight areas that bugs may hide in such as inside electrical outlets or other crevices.
It’s also important to empty the vacuum bag into an outdoor trash bin afterwards so no living eggs remain unaffected within your home. When using steamers, it is essential that temperatures of at least 113°F (45°C) for 3 seconds contact time is applied on all hard surfaces including furniture frames, walls and baseboards etc., which poses less risk of damaging materials than harsher chemical treatments do. Lastly—don’t forget about mattress seams! Both vacuums and steamers should not only kill any adult bedbugs but can potentially turn up their hiding spots allowing you complete coverage from even more sneaky pests!
3. Cold treatment: Utilizing freezing temperatures to eliminate bed bugs
Cold treatment is a non-chemical method of eliminating bed bugs. This approach utilizes extremely low temperatures to kill the insects, their eggs, and other related organisms. The most common cold treatments involve liquid nitrogen or cooling with CO2 snow which can reach a temperature below -26°C for at least 4 hours in order to be effective against bed bug elimination.
Extremely cold temperatures have proven highly successful when it comes to killing all stages of these pests in residential settings such as apartments and dwellings. It is also cost efficient since no product application costs are incurred unlike chemical methods that require costly products every time they’re used on infested areas.
4. Mechanical methods: Using traps, interceptors, and barriers to capture and prevent bed bug movement
Mechanical methods are the most widely used non-chemical treatment for bed bug infestations. Traps, interceptors, and barriers can be helpful in controlling an existing population while preventing more from entering a particular space.
Bed bug traps provide protection against invasions by luring adult bugs into sticky or electrically charged glueboards that capture them when they make contact with it.
Interceptor devices act as physical barriers between objects such as beds and furniture to stop bedbugs climbing up onto them during their nightly activities; these perimeter defense systems help break the breeding cycle of established populations too. Furthermore, chemical treatments found on carpets may prevent spreadable islets if applied correctly after vacuuming rugs thoroughly beforehand
Chemical Bed Bug Treatment Methods
1. Insecticides
Insecticides remain the primary chemical treatment used to eliminate bed bugs. Common insecticide formulations include dusts, aerosols (aka “bug bombs”), contact pesticides and residual sprays.
Dust-based products are usually applied in cracks and crevices where bug activity is likely occurring; while liquids may be spread across larger surface areas with a trigger spray bottle or broadcasted using specialty equipment like mist blowers or paint rollers.
When applying any product it’s important to read the label instructions carefully for appropriate use directions, coverage amounts and safety precautions/protocols relative to kids/pets/etc.
2. Sprays and dusts
Spray and dust insecticides are commonly used methods in chemical bed bug treatments. Insecticide sprays should be applied to cracks, crevices, baseboards, behind furniture legs and the perimeter of infested rooms.
Dusts can also be directly dusted into these areas or mixed with water for a more fine application spray around beds and carpets. After each treatment is completed it’s important to thoroughly vacuum all treated surfaces before leaving the area to ensure maximal effectiveness of your spraying efforts!
3. Residual insecticides
Residual insecticides are an effective way to provide long-term control of bed bugs. These products contain active ingredients that stay within the environment and can be applied as liquid or dust forms in infested areas.
They must always be used according to product instructions for optimal safety, such as readjusting applications when necessary and taking proper precautions when handling them around children and pets. Residuals work best in conjunction with other treatments, especially nonchemical ones like heat treatment or vacuuming, for a comprehensive approach to eliminating bed bug infestations.
4. Insecticide resistance
Insecticide resistance is a major concern when it comes to treating bed bugs. Insecticides should be used judiciously and rotated on an appropriate schedule in order to prevent the development of resistant colonies.
To reduce insecticide resistance, pest management professionals should keep records of all treatments applied, examine traps regularly for signs of live activity after applications have been made, monitor treated areas closely with regular intervals between subsequent applications or use baits alongside standard sprayed materials, and frequently switch active ingredients so that the same ingredient isn’t overused repeatedly.
These proactive measures will help ensure effective control while also preserving future efficacy against these difficult-to-control pests
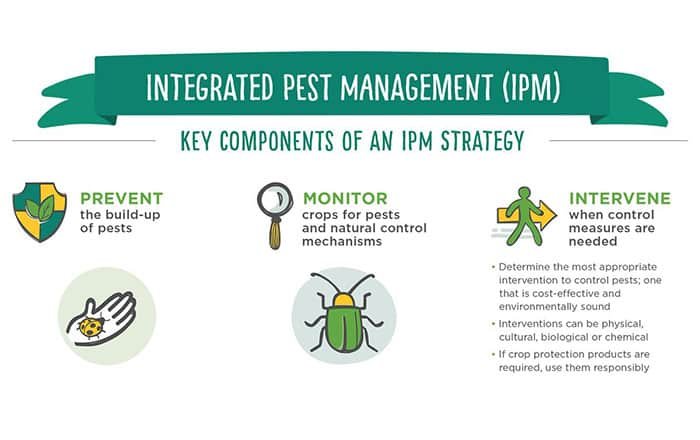
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approach
Definition and principles of IPM
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a sustainable approach to pest control that focuses on using multiple methods for prevention, elimination and management. This includes practices such as:
- Inspection, monitoring and record keeping
- Employing non-chemical means whenever possible
- Combining chemical treatments with other types of solutions when necessary while taking applicable safety precautions into account
- Minimizing disturbance in the environment to reduce present populations and prevent future infestation or recolonization opportunities
- Focusing on long-term goals rather than short term fixes
- Balance environmental stewardship with effective management of nuisance pests in an economically viable way
Combining non-chemical and chemical methods for optimal results
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an approach to bed bug control that combines non-chemical and chemical methods for optimal results. By using a combination of preventive measures, mechanical traps and interceptors, heat treatment, vacuuming and steaming techniques as well as insecticides, both immediate relief from infestation can be achieved while also ensuring sustained long-term protection against further spread.
IPM takes into account environmental concerns by reducing pesticide use where possible in favor of careful monitoring with follow up inspections when needed. Ultimately this makes it easier to prevent future outbreaks before they even occur whilst allowing the homeowner or business owner peace of mind knowing there are safe treatments available should any reinfestation become evident..
Monitoring and follow-up inspections for continued prevention
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic, evidence-based approach to long-term bed bug control that combines non-chemical and chemical methods. After the initial treatment, monitoring for new signs of infestation should be done regularly since early detection can prevent another spread.
Follow up inspections must also be conducted on certain areas where lingering activity may still exist such as cracks and crevices around furniture or behind walls. Lastly, preventive measures like vacuuming carpets and properly disposing garbage should always remain in everyday practice within the premises to maintain an environment free from pests over time.
Conclusion
A comprehensive and systematic approach to treating a bed bug infestation is the most effective way of eliminating them. All areas should be inspected first, followed by decluttering, containment and preparation measures that can reduce or eliminate potential hiding places for bed bugs.
Combining various treatments with the techniques mentioned above, give excellent results in getting rid of bedbugs completely from homes and workplaces quickly if used properly at the early stages of detection.
It’s important to note that ongoing monitoring needs regular checks over time so any future signs don’t go unchecked–early action gives you the best chance against successful eradication!